Two sample ttest with unequal variances in excel YouTube

Two-sample t-test (pooled-variance): Tails= two, Distribution= Student's t, Sample= Two samples, α= 0.05, Power= 0.8 , Effect Size= 0.5, Standard deviation=Equal &sigma. Example results: The sample size 64 for each group, will gain the power of 0.80146. (n1 = n2 = 64). Since the sample size is discrete, we look for the first n that gains the.
hypothesis testing ttest in large, unequal sample size + additional info such as effect size

Even though the sample sizes are unequal, the independent samples t-test and Welch's t-test both return similar results since the two samples had equal variances. Example 2: Unequal Sample Sizes and Unequal Variances. Suppose we administer two programs designed to help students score higher on some exam. The results are as follows: Program 1:
T test analysis is it always correct to compare means ? Easy Guides Wiki STHDA
In statistics, Welch's t-test, or unequal variances t-test, is a two-sample location test which is used to test the (null) hypothesis that two populations have equal means. It is named for its creator, Bernard Lewis Welch, is an adaptation of Student's t-test, and is more reliable when the two samples have unequal variances and possibly unequal sample sizes.
The empirical power of ttests under equal and unequal vari ances for... Download Table

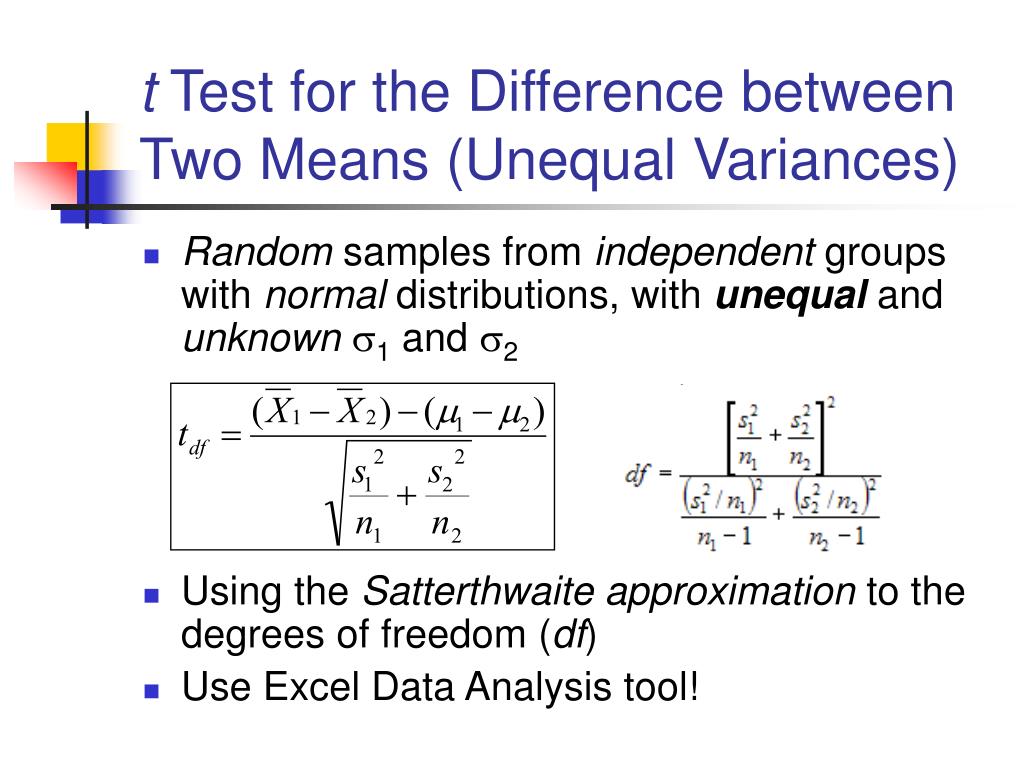
T-tests that assume equal variances of the two populations aren't valid when the two populations have different variances, & it's worse for unequal sample sizes. If the smallest sample size is the one with highest variance the test will have inflated Type I error). The Welch-Satterthwaite version of the t-test, on the other hand, does not.
Independent Samples Ttest Formula & Examples / How to Perform a ttest with Unequal Sample

Formulas for the test statistic in t-tests include the sample size, as well as its mean and standard deviation. The exact formula depends on the t-test type — check the sections dedicated to each particular test for more details.. Two-sample t-test if variances are unequal (Welch's t-test).
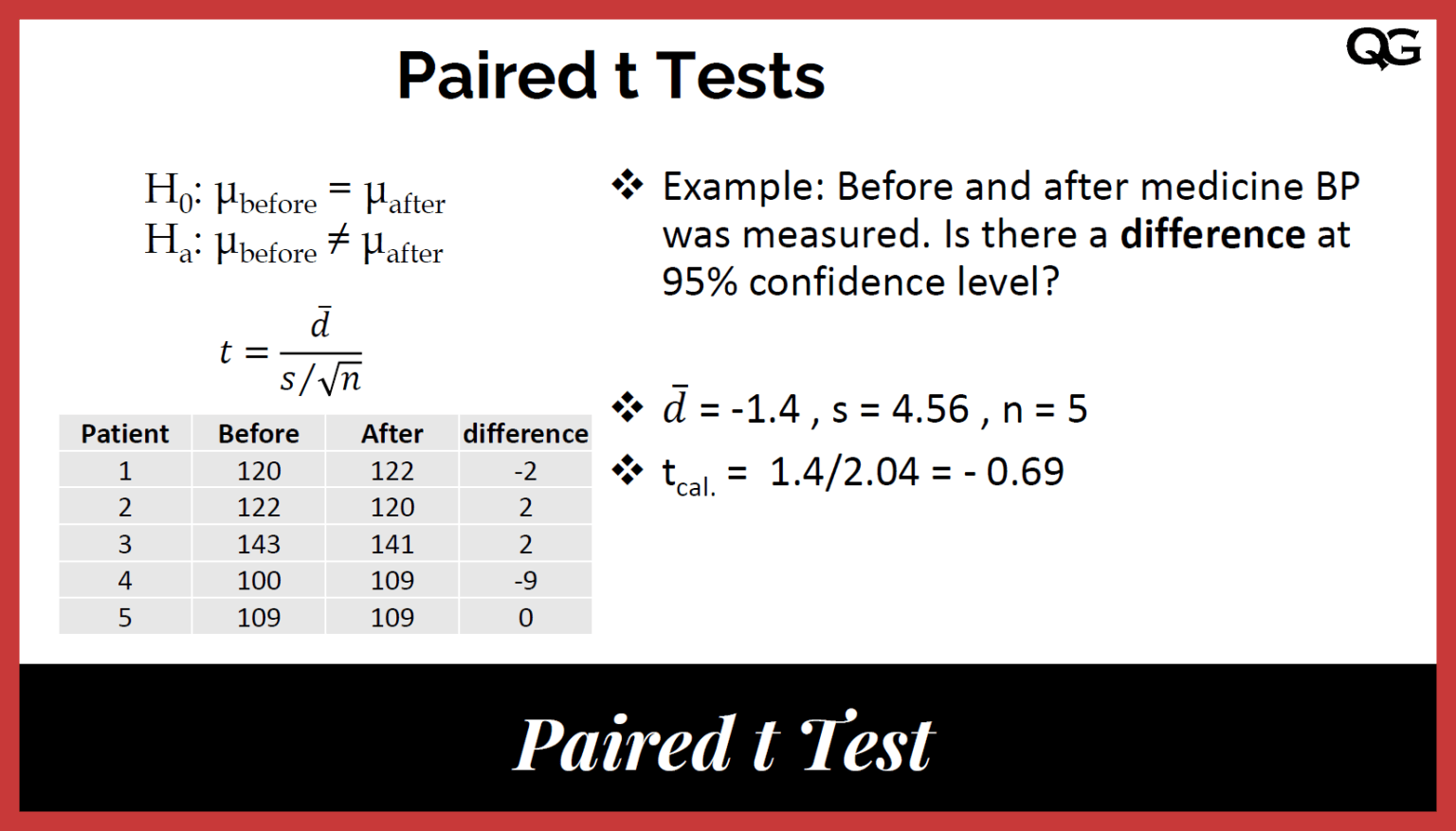
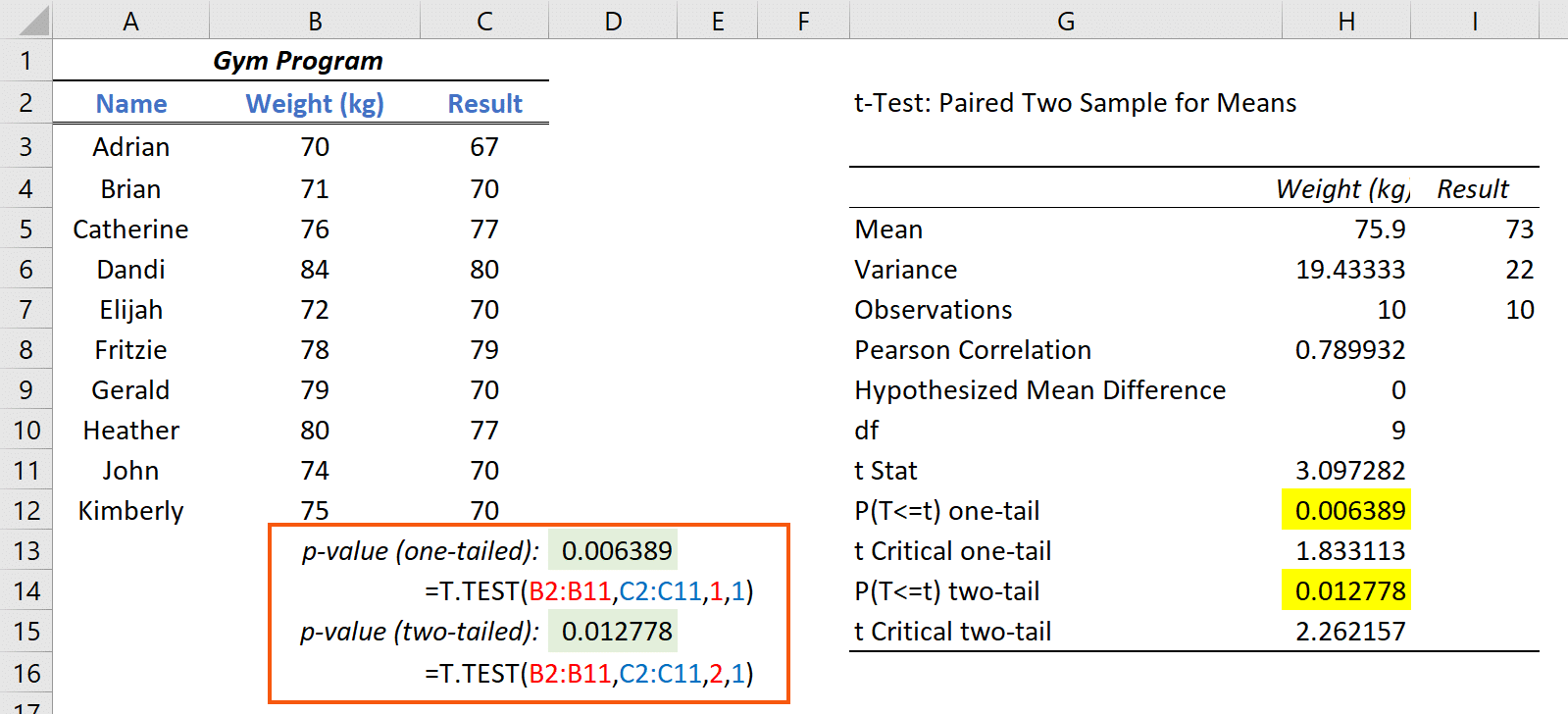
Paired tTest (Dependent Samples) Quality Gurus
The test is developed as an exact test that allows for unequal sample sizes and unequal variances of two populations. The exact property still holds even with small extremely small and unbalanced sample sizes (e.g. n 1 = 5 , n 2 = 50 {\displaystyle n_{1}=5,n_{2}=50} ).
Hypothesis TestingT Test From The GENESIS

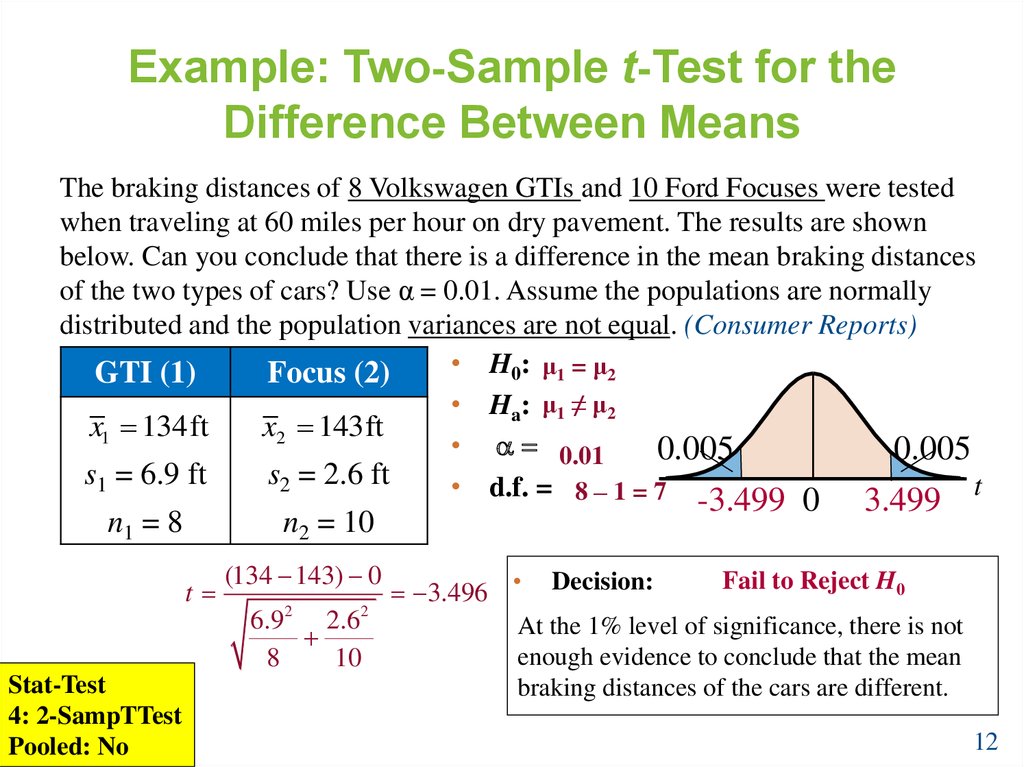
Variations of the t-Test: 2 Sample 2 tail 1 2 Sample t-Test (unequal sample sizes and unequal variances) Like the last example, below we have ceramic sherd thickness measurements (in cm) of two samples representing different decorative styles from an archaeological site. However, this time we see that the sample sizes are different, but we are.
T Test Example
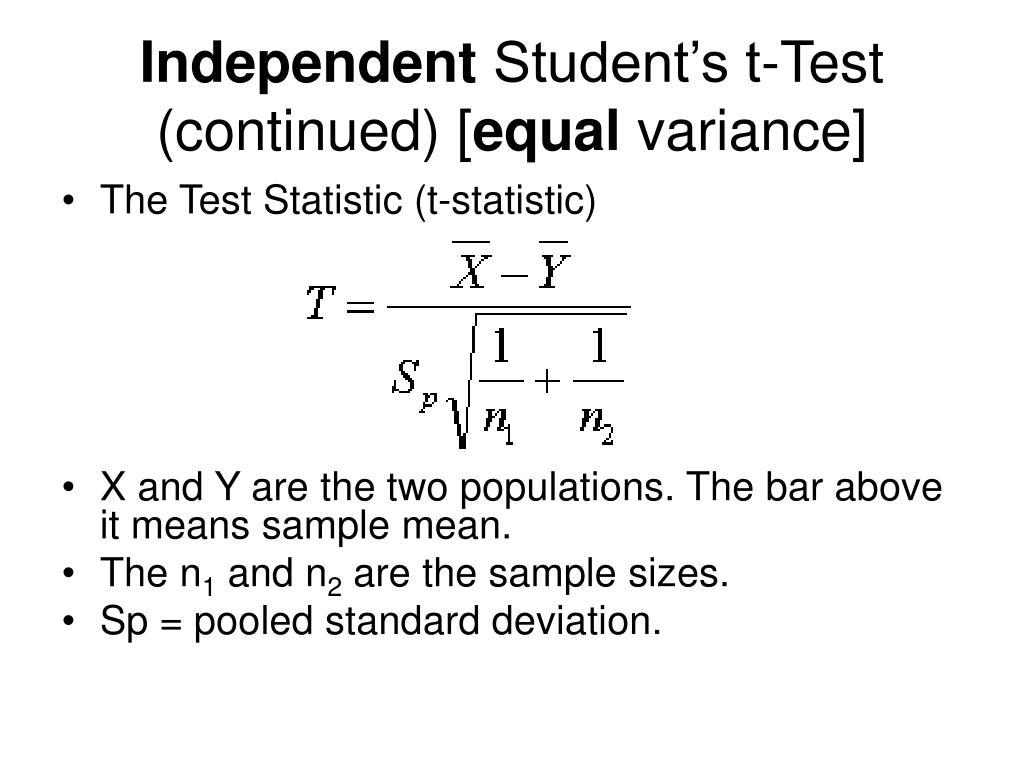
We do this in R with a Fisher's F-test, var.test(x, y). If your p > 0.05, then you can assume that the variances of both samples are homogenous. In this case, we run a classic Student's two-sample t-test by setting the parameter var.equal = TRUE. If the F-test returns a p < 0.05, then you can assume that the variances of the two groups are.
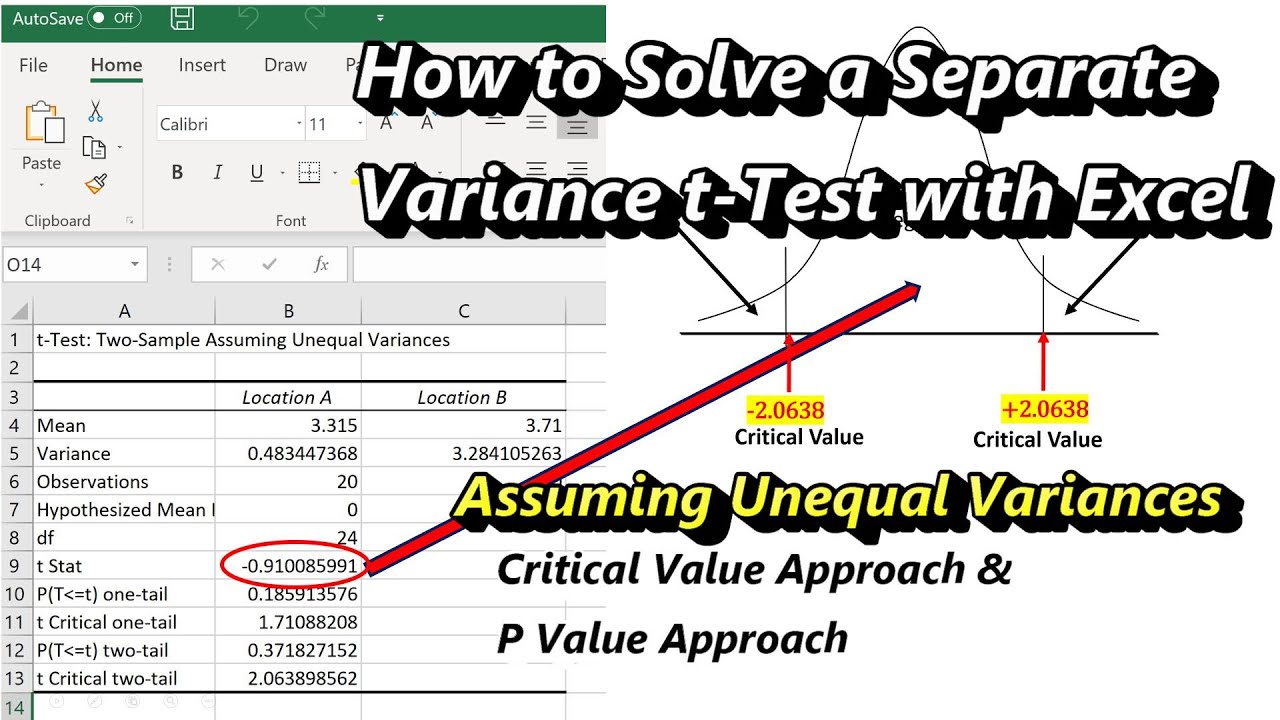
TTest for Unequal Variances Using Excel Comparing the Means of Two Independent Populations
The t-test is not one test, but a group of tests that constitutes all statistical tests distribute as t-distribution (Student's t-distribution). We use the t-test (s) to compare the sample average (Mean) to the known mean or to compare the averages of two groups when we don't know the standard deviation, and use the sample standard deviation.
Two sample unequal variance t test wescount
Given the following parameters, how do I calculate the effect size of an independent unequal sample size t test? sample 1: size = 32 mean = 845.1 std = 46.7 sample 2: size = 53 mean = 829.1 std = 33.8 test results: tstat = 1.83 p value = .035 df = 83
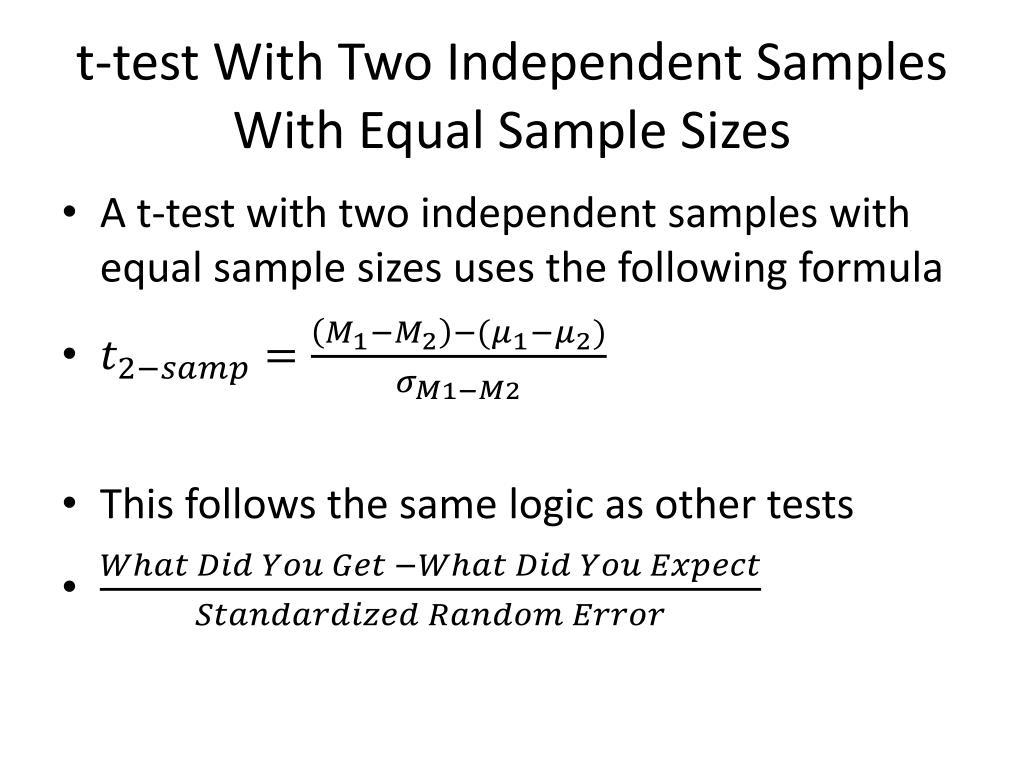
PPT ttest With Two Independent Samples With Equal Sample Sizes PowerPoint Presentation ID
If 'auto', it will automatically uses Welch T-test when the sample sizes are unequal, as recommended by Zimmerman 2004. r float. Cauchy scale factor for computing the Bayes Factor. Smaller values of r (e.g. 0.5), may be appropriate when small effect sizes are expected a priori; larger values of r are appropriate when large effect sizes are.
Hypothesis testing two sample t test (unequal variance) YouTube

3. Theoretically, if the assumption of equal variances is satisfied and the dependent variable is normally distributed you could run a t-test despite the unequal sample sizes between the two comparison groups. I suggest you read these two posts ( 1 & 2) which deal with similar issues.
PPT Chapter 2 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID677906
A t test compares the means of two groups. There are several types of two sample t tests and this calculator focuses on the three most common: unpaired, welch's, and paired t tests. Directions for using the calculator are listed below, along with more information about two sample t tests and help on which is appropriate for your analysis. NOTE: This is not the same as a one sample t test; for.
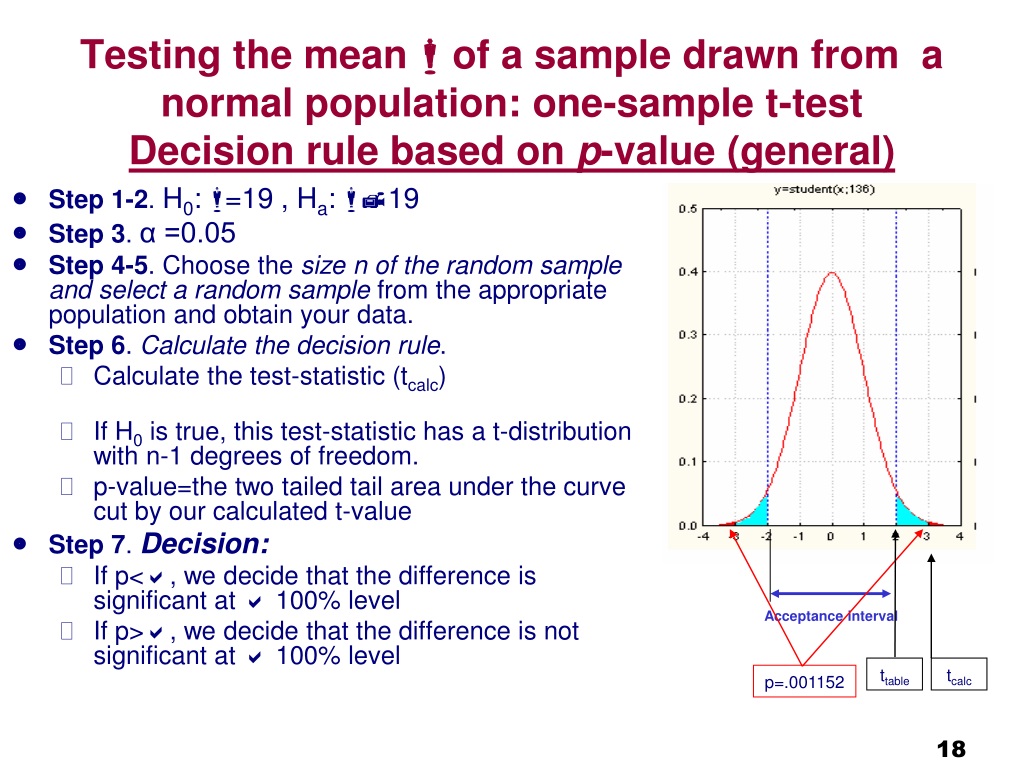
PPT Hypothesis tests I . One sample t test , paired ttest PowerPoint Presentation ID9733964
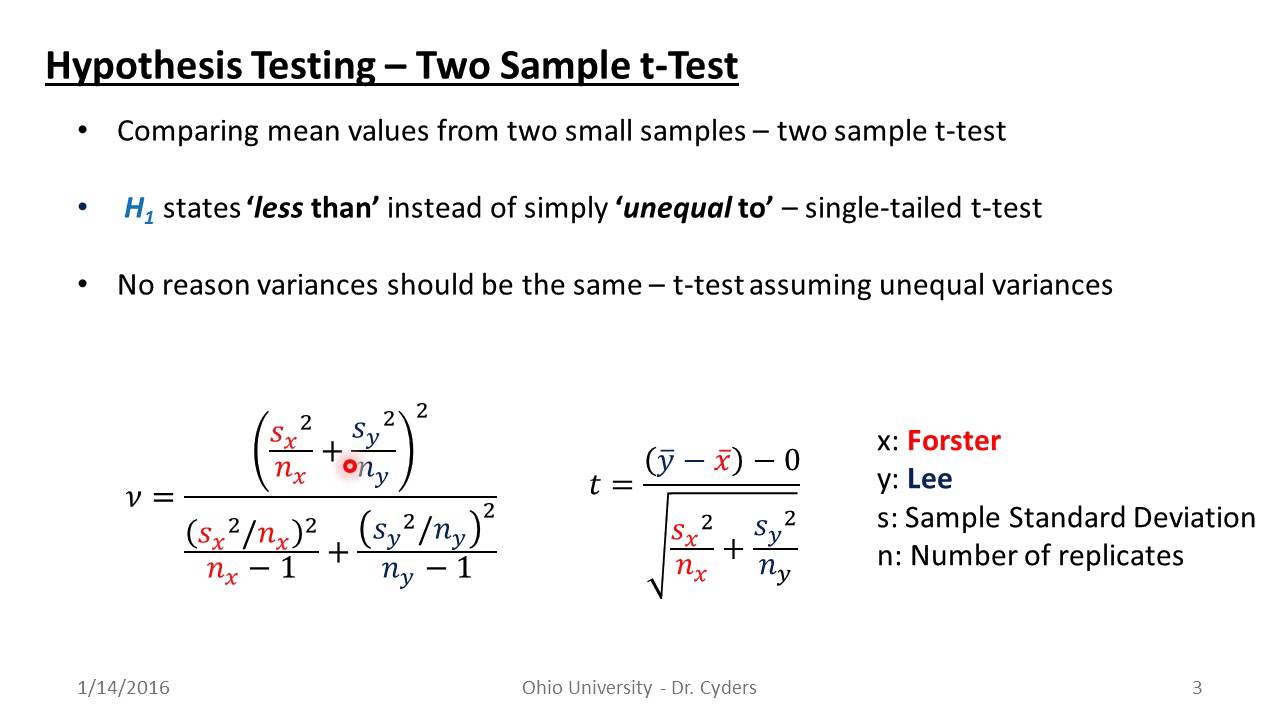
If you have unequal variances and unequal sample sizes, it's vital to use the unequal variances version of the two sample t test! Related post: Standard Deviations. Example Independent Samples T Test. Let's run an example independent sample t test! Our hypothetical scenario is that we are comparing scores from two teaching methods.
Two sample unequal variance t test excel type ownamela
Welch's t-test is more reliable when the 2 samples have unequal variances and/or unequal sample sizes. We need to maintain the assumption of normality. Because the population variances are not equal, we have to estimate them separately by 2 sample variances, s 1 2 and s 2 2. As the result, the form of t-test statistic is given as follows;
Hypothesis Testing Example Two Sample tTest YouTube
Revised on June 22, 2023. A t test is a statistical test that is used to compare the means of two groups. It is often used in hypothesis testing to determine whether a process or treatment actually has an effect on the population of interest, or whether two groups are different from one another. t test example.